Docker Compose #
Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications using a declarative YAML file called docker-compose.yml. It makes it easy to configure, manage, and scale containerized applications by providing a simple way to define each service, its dependencies, and how they should interact.
In this section, we’ll set up a LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP) using Docker Compose to deploy a PHP website available on the web.
Creating the Docker Compose File #
Create a new file named docker-compose.yml in your project directory and add the following content:
services:
web:
image: php:8.1-apache
volumes:
- ./public:/var/www/html
ports:
- "80:80"
depends_on:
- db
db:
image: mysql:8.0
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: my_root_password
MYSQL_DATABASE: my_database
MYSQL_USER: my_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: my_password
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
phpmyadmin:
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
ports:
- "8080:80"
environment:
PMA_HOST: db
PMA_USER: my_user
PMA_PASSWORD: my_password
depends_on:
- db
volumes:
db_data:
This docker-compose.yml file defines three services:
web: This service uses the
php:8.1-apacheimage and maps thepublicdirectory on the host to the Apache document root/var/www/htmlinside the container. It also exposes port 80 on the host.db: This service uses the
mysql:8.0image and sets up environment variables for the root password, database name, and user credentials. It creates a named volumedb_datato persist the MySQL data.phpmyadmin: This service uses the
phpmyadmin/phpmyadminimage to provide a web interface for managing the MySQL database. It exposes port 8080 on the host and sets up environment variables for the database connection.
Creating the PHP Website #
Create a new directory named public in your project directory and add your PHP files there. For example, you can create a simple index.php file with the following content:
<?php
$conn = new mysqli('db', 'my_user', 'my_password', 'my_database');
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
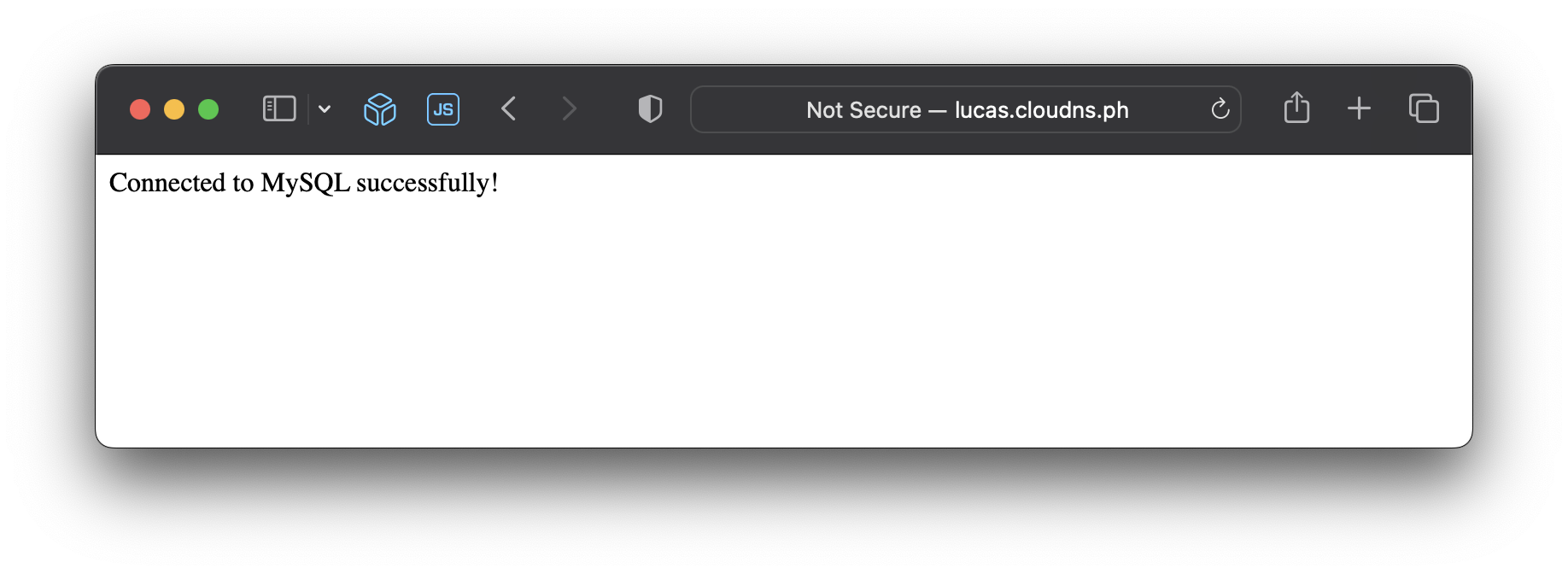
echo "Connected to MySQL successfully!";
This PHP script connects to the MySQL database using the credentials defined in the docker-compose.yml file.
Running the LAMP Stack #
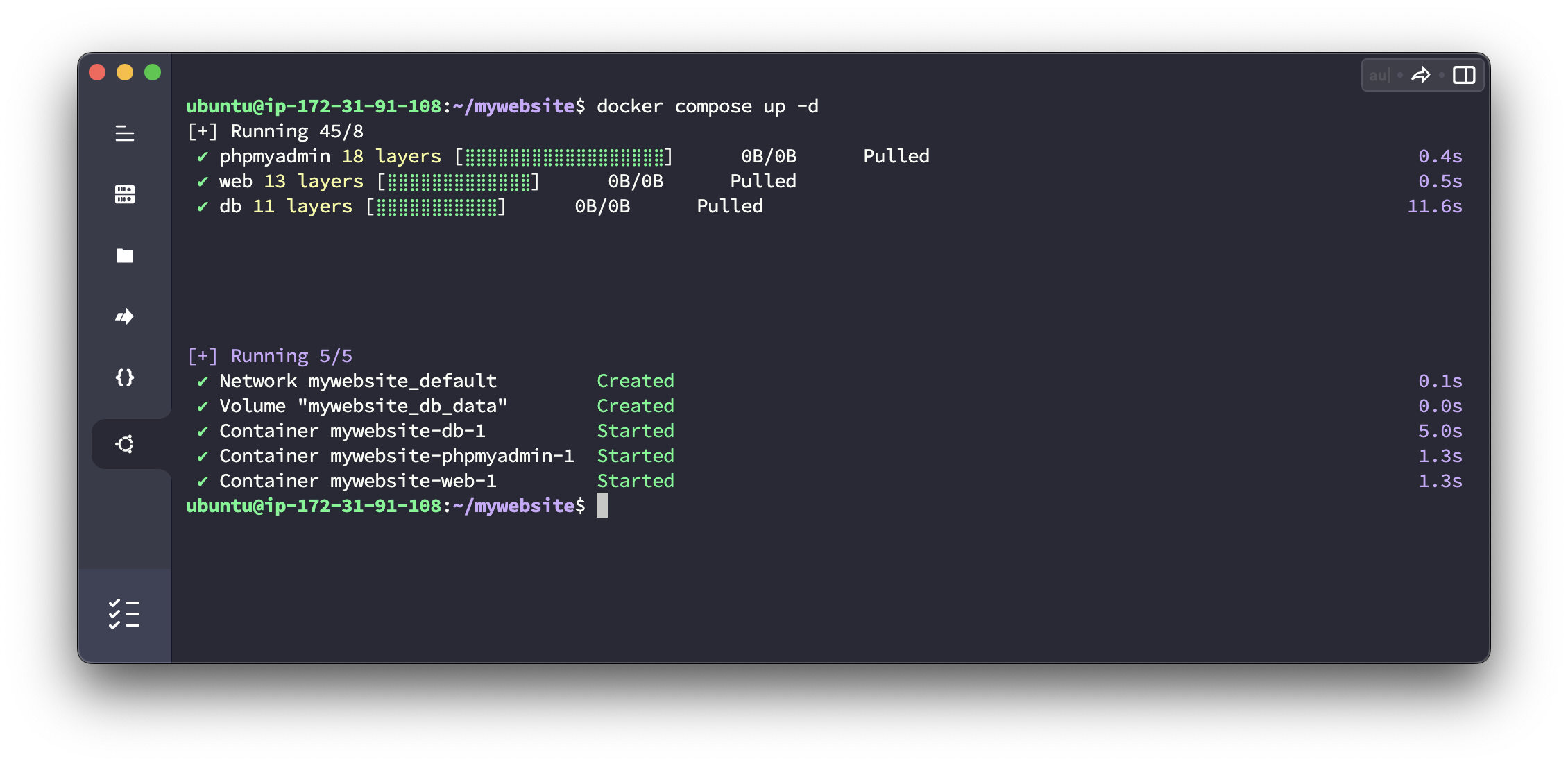
In your terminal, navigate to the project directory containing the docker-compose.yml file and run the following command:
docker-compose up -d
Docker Compose will pull the required images, create the containers, and set up the network connections as defined in the docker-compose.yml file.
Once the containers are running, you can access the PHP website at your public DNS address.
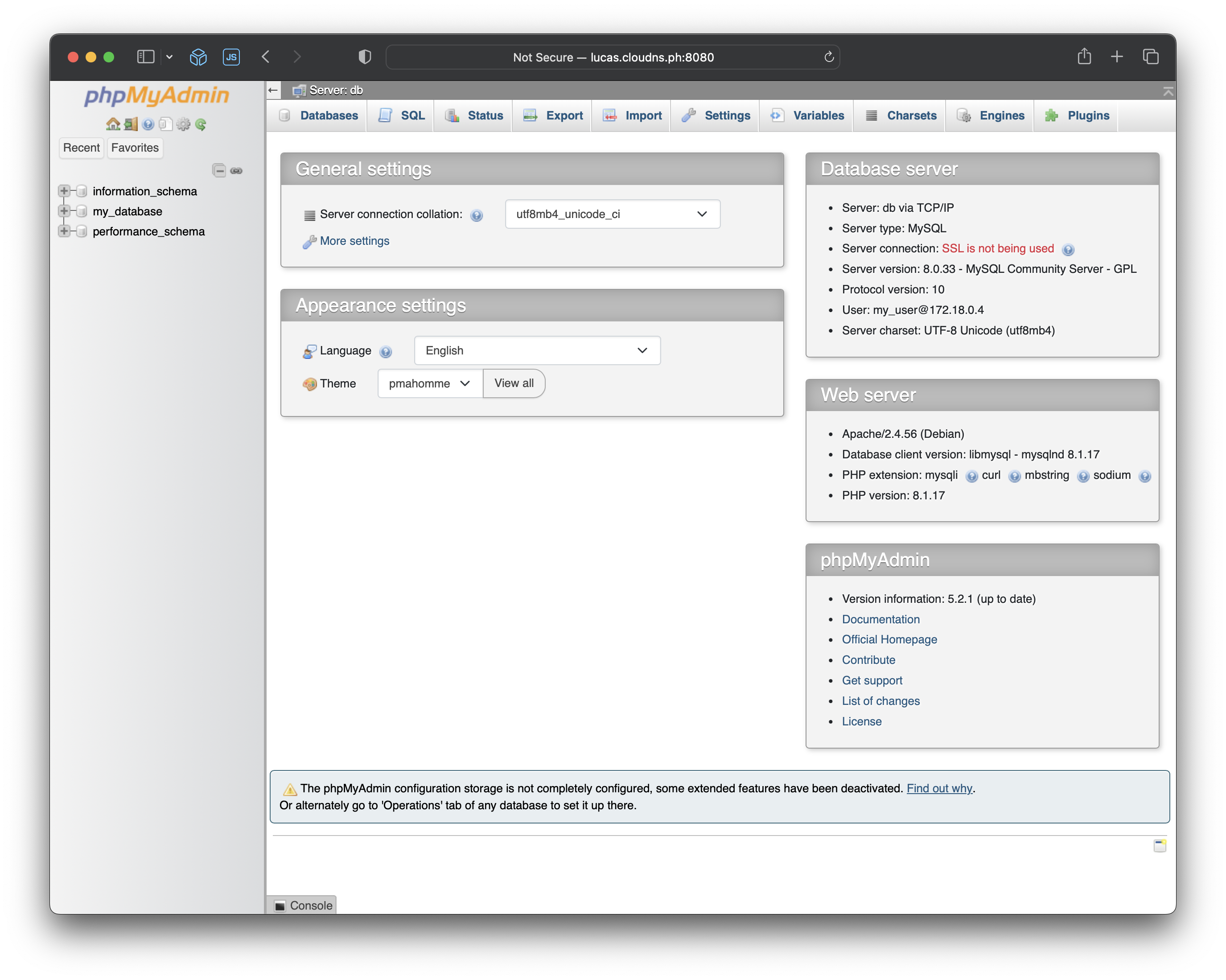
The phpMyAdmin interface should be available on port :8080.
To stop the containers, run the following command in the project directory:
docker-compose down
This command will stop and remove the containers, networks, and any anonymous volumes created by docker-compose up. Note that the named volume db_data will not be removed automatically to ensure data persistence. If you want to remove the named volumes as well, you can use the --volumes or -v flag:
docker-compose down --volumes
Keep in mind that using this flag will delete the named volumes and all the data stored in them.
Docker Compose simplifies the process of managing and running multi-container applications. By defining the services, volumes, and network connections in a single docker-compose.yml file, we can easily start, stop, and scale our application as needed.